Control of overrun of the subscribed power
Reduce your subscribed power and avoid exceeding it by controlling the connection and disconnection of non-critical loads

< 2 years

4% - 15% average savings on the bill
Application areas
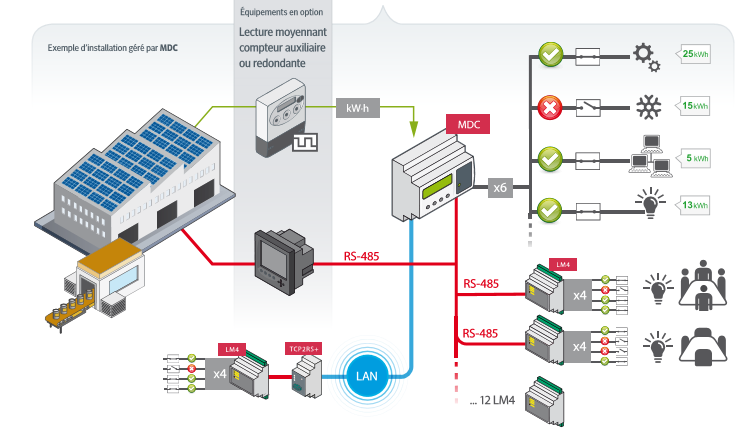
Diagram : Control of the overrun of the subscribed power
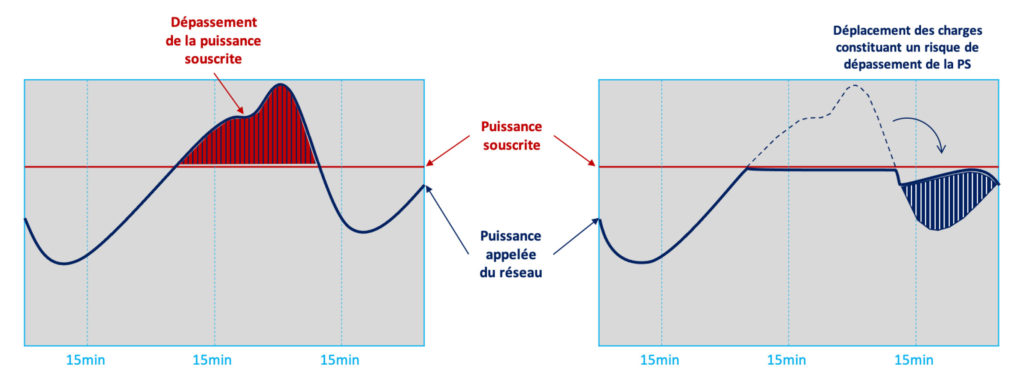
Subscribed power charges and penalties for exceeding subscribed power are one of the main items on the electricity bills of high and medium voltage customers.
To reduce their bill, users are encouraged to subscribe to the lowest possible power level and not to exceed it too much. To do this, they must
control
the simultaneous power calls of their loads and machines.
The difficulty is that the power demand is not an instantaneous value, but rather an average calculated by the energy meter over successive periods of 10 to 15 minutes, depending on the country,
The peak load management system is a system capable of predicting the risk of exceeding the subscribed power sufficiently in advance, disconnecting non-priority loads at controlled times and avoiding their simultaneous reconnection when the risk of exceeding the subscribed power disappears. This is equivalent to “shifting” the operation of certain loads over time.
Applications
All types of industries
Tertiary buildings with medium-voltage connections
The loads to be disconnected should be selected from those that do not affect the company’s main production process, for example:
- Lighting,
- Air conditioning,
- Fans and extractors,
- Cold compressors,
- Pumps for feeding storage tanks,
- Packaging machines,
- Crushers or grinders in certain processes (quarry, mine,…)
- etc.
Benefits of our solution
- Control of up to 48 different outlets
- Integrated web server and software with real time visualization of the plant operation
- Management according to fully configurable time slots, calendar or pre-programmed conditions
- Programming of several power limits per time slot
- Manual or automatic operation management
- Local or remote control of loads
- Prioritization of loads (connection / disconnection) with creation of load groups